What Is the Flu?
The flu, also called influenza, is a common viral infection. It affects your nose, throat, and sometimes your lungs. Many people get the flu each year, especially during the colder months. Because the flu spreads easily, it can cause outbreaks in schools, offices, and communities. Understanding flu and vaccinations can help you stay healthy and protect others.
Common Symptoms of the Flu
Flu symptoms often appear suddenly. While some people have mild symptoms, others may feel very sick. Here are the most common signs:
However, not everyone with the flu will have a fever. If you notice these symptoms, it is important to rest and stay hydrated.
How the Flu Spreads
The flu virus spreads mainly through tiny droplets. When someone with the flu coughs, sneezes, or talks, these droplets can land in the mouths or noses of people nearby. Sometimes, you can also get the flu by touching a surface with the virus and then touching your mouth, nose, or eyes. Because the flu spreads so easily, prevention is key.
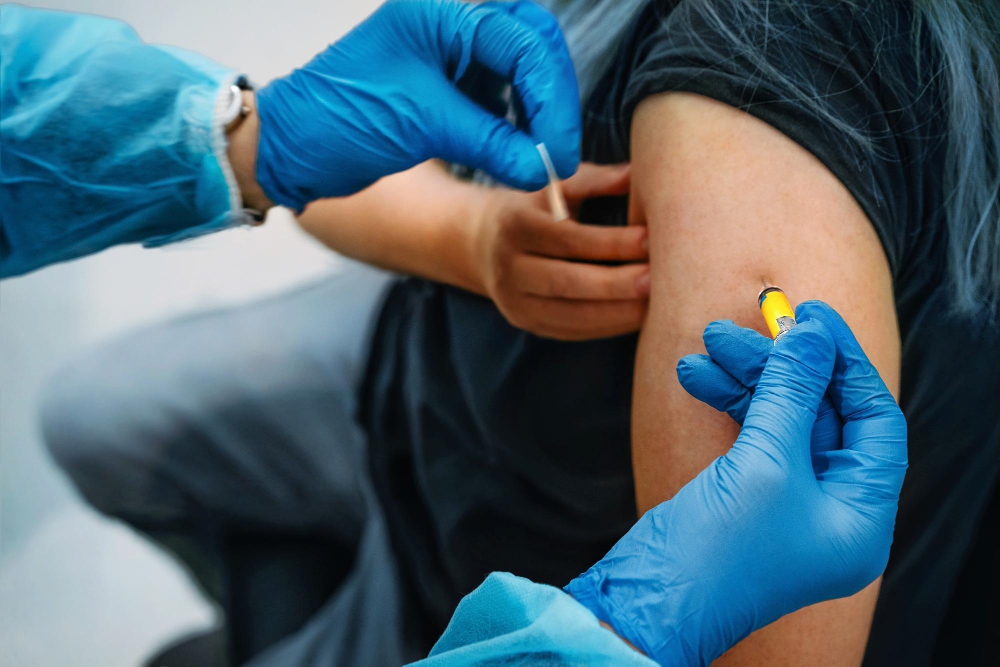
Importance of Flu Vaccinations
Flu vaccinations are the best way to protect yourself and others. Each year, the flu vaccine is updated to fight the most common strains. According to the CDC and WHO, getting vaccinated lowers your risk of getting sick, missing work or school, and spreading the virus to others. In addition, flu vaccines help protect people who are more likely to get very sick, such as young children, older adults, and those with health problems.
Who Should Get Vaccinated?
Almost everyone over six months old should get a flu shot each year. However, some groups need it even more:
Even if you are healthy, getting vaccinated helps protect those around you.
Types of Flu Vaccines Available
There are several types of flu vaccines. Most people get the flu shot, which is given with a needle in the arm. Some children and adults can get a nasal spray vaccine. Your doctor can help you choose the best option. In some places, high-dose vaccines are available for older adults. Because the flu virus changes, you need a new vaccine each year.
Safety and Effectiveness of Flu Vaccines
Flu vaccines are safe and well-tested. Most people have no side effects, or only mild ones like a sore arm or low fever. Serious reactions are very rare. The CDC and WHO both recommend yearly flu shots for most people. While the vaccine may not prevent all cases, it makes illness milder and lowers the risk of serious problems. Studies show that flu vaccines prevent thousands of hospital stays each year.
Myths and Facts About Flu Vaccinations
Many myths about flu and vaccinations can cause confusion. Let’s clear up some common ones:
Prevention Tips and Healthy Habits
Besides getting vaccinated, you can take other steps to prevent the flu. Try these flu prevention tips:
These habits, along with the flu vaccine, offer the best protection.
When to See a Doctor
Most people recover from the flu at home. However, you should see a doctor if you:
Young children, older adults, and people with health problems should seek help sooner. Early treatment can prevent serious complications.
Conclusion
Flu and vaccinations are important topics for everyone. Because the flu spreads easily, staying informed helps protect you and your loved ones. For the best advice about flu vaccine benefits, flu shot safety, and flu prevention tips, consult a healthcare provider for personalized advice about flu and vaccinations.